Have you ever wondered if birds are mammals? It’s a question that might seem simple at first, but the answer reveals some surprising facts about how animals are classified.
You might notice birds and mammals share a few things—they both have backbones and keep their bodies warm—but they also have key differences that set them apart. If you want to understand what really makes a bird a bird, and why they don’t belong to the mammal family, keep reading.
By the end, you’ll see how these fascinating creatures fit into the animal kingdom—and why their story is more interesting than you think.

Credit: www.activewild.com
Birds And Mammals Compared
Birds and mammals are two distinct groups of animals. Both share some common traits like being warm-blooded and having backbones. Yet, they have many unique features that set them apart. Understanding these differences helps explain why birds are not mammals.
Body Covering Differences
Birds have feathers covering their bodies. Feathers help with flight, insulation, and display. Mammals have hair or fur instead. Hair keeps mammals warm and protects their skin. Feathers and hair are very different in structure and function.
Reproductive Methods
Birds lay eggs with hard shells. These eggs are usually kept in nests until they hatch. Most mammals give birth to live young. Mammals develop their babies inside the mother’s body before birth. These reproductive methods show clear differences between the two groups.
Nourishment Of Young
Birds do not produce milk for their young. They feed their chicks with food they catch or find. Mammals have mammary glands that produce milk. This milk is the main food for newborn mammals. Feeding young with milk is a key mammal trait.
Mouth Structures
Birds have beaks without teeth. Beaks vary in shape depending on their diet. Mammals usually have teeth to chew food. Teeth come in different types like incisors and molars. This difference helps identify birds and mammals easily.
Credit: outforia.com
Traits Birds And Mammals Share
Birds and mammals share several important traits despite belonging to different animal classes. These common features help both groups survive in diverse environments. Understanding these shared traits clarifies why birds are not mammals, yet still have similarities. Let’s explore these traits one by one.
Warm-blooded Nature
Both birds and mammals are warm-blooded animals. This means they keep their body temperature steady, no matter the weather. Warm-bloodedness helps them stay active in cold or hot climates. It also supports high energy levels and fast movements. This trait is rare among animals and shows a key similarity between birds and mammals.
Air Breathing
Birds and mammals breathe air through lungs. They take in oxygen to power their bodies and release carbon dioxide. Their lungs are efficient and allow them to live on land. Breathing air is different from fish, which use gills. This shared trait shows how both groups adapted to life outside water.
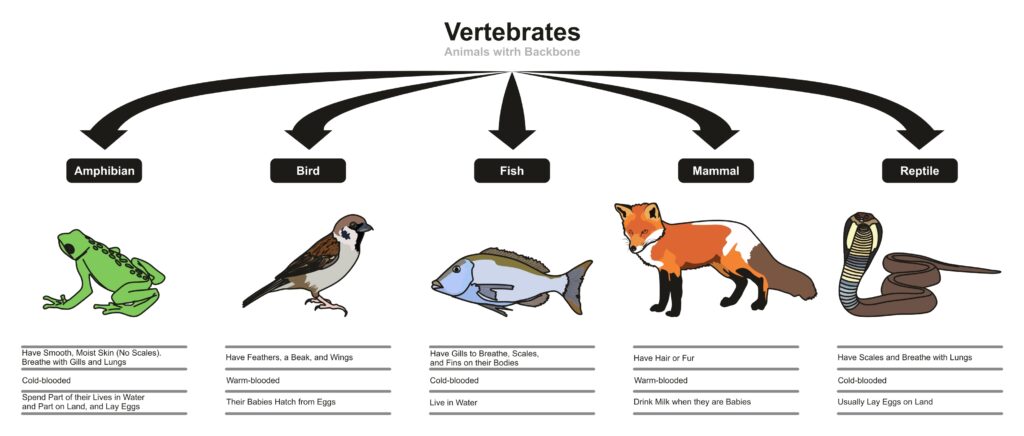
Backbone Presence
Both birds and mammals have backbones, making them vertebrates. The backbone protects the spinal cord and supports the body. It allows complex movements and physical strength. Having a backbone is a major step in animal evolution. This trait connects birds and mammals to many other animals, like reptiles and amphibians.
Classification Of Birds
Birds belong to a distinct group in the animal kingdom. Their classification sets them apart from mammals and other creatures. Understanding this classification helps clarify why birds are not mammals.
Scientists classify living things by grouping them based on shared traits. Birds have unique features that place them in their own class. This section explains their classification from kingdom to class and highlights what makes birds special.
Kingdom To Class Levels
Birds belong to the kingdom Animalia, which includes all animals. They fall under the phylum Chordata, meaning they have a backbone. Within Chordata, birds are part of the class Aves.
The class Aves is separate from Mammalia, the class for mammals. Birds evolved differently and have traits unique to their group. This classification helps scientists study and understand birds better.
Unique Bird Features
Feathers are a key feature found only in birds. They help with flight, temperature control, and display. Birds also have beaks instead of teeth, which varies by species.
Birds lay hard-shelled eggs, unlike most mammals that give live birth. They have lightweight bones to aid flying. Their respiratory system is highly efficient for breathing during flight.
Warm-blooded like mammals, birds maintain a steady body temperature. These features clearly show why birds belong to their own class and are not mammals.
Bird Evolution And Ancestry
Bird evolution traces a fascinating journey from ancient creatures to the diverse species we see today. Understanding their ancestry helps reveal why birds differ from mammals despite some shared traits. Birds evolved over millions of years through adaptations that suited survival in various environments. Their lineage connects deeply with prehistoric life, especially dinosaurs and reptiles.
Dinosaur Connection
Birds share a close link with certain dinosaurs, especially theropods. These dinosaurs walked on two legs and had hollow bones, features that birds also possess. Fossils show feathers on some dinosaurs, hinting at the origin of bird feathers. This connection places birds as modern descendants of these ancient creatures. Birds inherited many traits from their dinosaur ancestors, including their skeletal structure and metabolism.
Relation To Reptiles
Birds are more closely related to reptiles than mammals. They belong to a group called archosaurs, which includes crocodiles and dinosaurs. Like reptiles, birds lay eggs with hard shells and have scales on their legs. Their lungs and heart structure also show reptile-like features. Despite being warm-blooded, birds retain many reptilian characteristics, linking them firmly to this group. This ancestry explains why birds are not classified as mammals.
Bird Groups And Orders
Birds are divided into many groups based on their features and behaviors. These groups help scientists organize the vast variety of birds. Each group shares common traits that set them apart from others.
Understanding bird groups and orders clarifies how birds differ from mammals. Birds belong to the class Aves, which splits further into orders and families. This system shows the rich diversity among birds.
Major Bird Orders
Birds fall into several main orders. Each order groups birds with similar characteristics. For example, Passeriformes includes songbirds like sparrows and finches. Another order, Accipitriformes, covers birds of prey such as eagles and hawks.
Other notable orders include Anseriformes, which contains ducks and geese, and Strigiformes, the owls. These orders help identify birds by their habits, shapes, and habitats.
Family And Species Levels
Within each order, birds are further divided into families. Families group birds that are even more closely related. For example, within the order Passeriformes, the family Corvidae includes crows and ravens.
Species is the most specific level. Each species has unique traits and behaviors. This system helps scientists and bird watchers recognize and study birds accurately.

Credit: www.birdfy.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Birds Mammals Yes Or No?
No, birds are not mammals. Birds belong to class Aves, have feathers, lay eggs, and lack mammary glands. Mammals have hair or fur, give live birth mostly, and produce milk. Both are warm-blooded vertebrates but evolved differently.
What Are Birds Classified?
Birds belong to the class Aves, characterized by feathers, beaks, wings, and laying hard-shelled eggs. They are warm-blooded vertebrates, closely related to reptiles but distinct from mammals.
Is A Bird A Reptile Or Mammal?
Birds are neither reptiles nor mammals; they belong to Class Aves. Birds have feathers, lay eggs, and lack mammary glands, unlike mammals. Birds share evolutionary roots with reptiles but differ significantly. They are warm-blooded vertebrates, distinct from mammals by their unique features like beaks and feathers.
Are Chickens Mammals?
No, chickens are not mammals. They belong to the bird class Aves, have feathers, lay eggs, and lack mammary glands.
Conclusion
Birds and mammals belong to different animal classes. Birds have feathers and lay eggs. Mammals have hair and mostly give live birth. Both are warm-blooded and breathe air. Birds share more traits with reptiles than mammals. Knowing these facts helps clear common confusion.
Understanding animal groups makes nature more interesting. Birds are unique creatures worth appreciating.

